Introduce
TLS的设计目标是构建一个安全传输层(Transport Layer Security ),在基于连接的传输层(如TCP)之上提供:
- 密码学安全
- 保密, Message Privacy (保密通过加密encryption实现,所有信息都加密传输,第三方无法窃听 )
- 完整性, Message Integrity( 通过MAC校验机制,一旦被篡改,通信双方会立刻发现 )
- 认证, mutual Authentication (双方认证,双方都可以配备证书,防止身份被冒充 )
- 互操作,通用性 ( 根据公开的RFC,任何符合RFC的软件实现都可以互操作,不受限于任何专利技术)
- 可扩展性 ( 通过扩展机制 tls_ext可以添加功能,有大量的新功能,都是通过扩展添加的)
- 高效率 (通过 session cache,恰当部署cache之后,TLS的效率很高)
History
- 1995: SSL 2.0, 由Netscape提出,这个版本由于设计缺陷,并不安全,很快被发现有严重漏洞,已经废弃。
- 1996: SSL 3.0. 写成RFC,开始流行。目前(2015年)已经不安全,必须禁用。
- 1999: TLS 1.0. 互联网标准化组织ISOC接替NetScape公司,发布了SSL的升级版TLS 1.0版.
- 2006: TLS 1.1. 作为 RFC 4346 发布。主要fix了CBC模式相关的如BEAST攻击等漏洞
- 2008: TLS 1.2. 作为RFC 5246 发布 。增进安全性。目前(2015年)应该主要部署的版本,请确保你使用的是这个版本
- 2015之后: TLS 1.3,还在制订中,支持0-rtt,大幅增进安全性,砍掉了AEAD之外的加密方式
Handshake

False Start
False Start 有抢跑的意思,意味着不按规则行事。TLS False Start 是指客户端在发送 Change Cipher Spec Finished 同时发送应用数据(如 HTTP 请求),服务端在 TLS 握手完成时直接返回应用数据(如 HTTP 响应)。这样,应用数据的发送实际上并未等到握手全部完成,故谓之抢跑。这个过程如下图所示:

Session Reuse

SessionID
SessionTicket
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5077
https://github.com/vincentbernat/rfc5077 - Various tools for testing RFC 5077
Forward Secrecy
Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman vs static Diffie-Hellman
Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman (DHE in the context of TLS) differs from the static Diffie-Hellman (DH) in the way that static Diffie-Hellman key exchanges always use the same Diffie-Hellman private keys. So, each time the same parties do a DH key exchange, they end up with the same shared secret.
When a key exchange uses Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman a temporary DH key is generated for every connection and thus the same key is never used twice. This enables Forward Secrecy (FS), which means that if the long-term private key of the server gets leaked, past communication is still secure.
This distinction also holds for the Elliptic Curve variants ECDHE (ephemeral, provides Forward Secrecy) and ECDH (static).
Due to increasing concern about pervasive surveillance, key exchanges that provide Forward Secrecy are recommended, see for example RFC 7525, section 6.3.
https://tls.mbed.org/kb/cryptography/ephemeral-diffie-hellman
DH Parameters
$ openssl dhparam -out dhparam4096.pem 4096
ssl_dhparam dhparam4096.pem;
HSTS
Spec:
h
通过 h
HPKP
- h
t - Analyse your HPKP policyt p s : / / r e p o r t - u r i . i o / h o m e / p k p _ a n a l y s e / - h
t - HTTP Public Key Pinning (HPKP)t p s : / / d e v e l o p e r . m o z i l l a . o r g / e n - U S / d o c s / W e b / H T T P / P u b l i c _ K e y _ P i n n i n g
Certificate Transparency
https://www.certificate-transparency.org/
- https://crt.sh/
- https://censys.io/certificates
- https://www.google.com/transparencyreport/https/ct/
- https://ct.tacticalsecret.com/
- https://github.com/jcjones/ct-sql
- https://uninvited-guests.github.io/ - ninvited Guests: Analyzing the Identity and Behavior of Certificate Transparency Bots
CAA
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6844
https://help.dyn.com/zone-records/#(CAA)
https://support.dnsimple.com/articles/caa-record/
https://blog.qualys.com/ssllabs/2017/03/13/caa-mandated-by-cabrowser-forum
GREASE
GREASE (Generate Random Extensions And Sustain Extensibility) is a proposal to reserves some currently unused values for clients to advertise at random. Correct server implementations will ignore these values and interoperate. Servers that do not tolerate unknown values will fail to interoperate with existing clients, revealing the mistake before it is widespread.
Version
SSL 1.0, 2.0, 3.0
SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)是网景公司(Netscape)设计的主要用于Web的安全传输协议,这种协议在Web上获得了广泛的应用。
基础算法由作为网景公司的首席科学家塔希尔·盖莫尔(Taher Elgamal)编写,所以他被人称为“SSL之父”。
2014年10月,Google发布在SSL 3.0中发现设计缺陷,建议禁用此一协议。攻击者可以向TLS发送虚假错误提示,然后将安全连接强行降级到过时且不安全的SSL 3.0,然后就可以利用其中的设计漏洞窃取敏感信息。Google在自己公司相关产品中陆续禁止向后兼容,强制使用TLS协议。Mozilla也在11月25日发布的Firefox 34中彻底禁用了SSL 3.0。微软同样发出了安全通告。
- 1.0版本从未公开过,因为存在严重的安全漏洞。
- 2.0版本在1995年2月发布,但因为存在数个严重的安全漏洞而被3.0版本替代。
- 3.0版本在1996年发布,是由网景工程师Paul Kocher、Phil Karlton和Alan Freier完全重新设计的。较新版本的SSL/TLS基于SSL 3.0。SSL 3.0作为历史文献IETF通过 RFC 6101 发表。
TLS 1.0
IETF将SSL标准化,即 RFC 2246 ,并将其称为TLS(Transport Layer Security)。从技术上讲,TLS 1.0与SSL 3.0的差异非常微小。但正如RFC所述"the differences between this protocol and SSL 3.0 are not dramatic, but they are significant enough to preclude interoperability between TLS 1.0 and SSL 3.0”(本协议和SSL 3.0之间的差异并不是显著,却足以排除TLS 1.0和SSL 3.0之间的互操作性)。TLS 1.0包括可以降级到SSL 3.0的实现,这削弱了连接的安全性。
TLS 1.1
TLS 1.1在 RFC 4346 中定义,于2006年4月发表,它是TLS 1.0的更新。在此版本中的差异包括:
- 添加对CBC攻击的保护:
- 隐式IV被替换成一个显式的IV。
- 更改分组密码模式中的填充错误。
- 支持IANA登记的参数。
TLS 1.2
TLS 1.2在 RFC 5246 中定义,于2008年8月发表。它基于更早的TLS 1.1规范。主要区别包括:
- 可使用密码组合选项指定伪随机函数使用SHA-256替换MD5-SHA-1组合。
- 可使用密码组合选项指定在完成消息的哈希认证中使用SHA-256替换MD5-SHA-1算法,但完成消息中哈希值的长度仍然被截断为96位。
- 在握手期间MD5-SHA-1组合的数字签名被替换为使用单一Hash方法,默认为SHA-1。
- 增强服务器和客户端指定Hash和签名算法的能力。
- 扩大经过身份验证的加密密码,主要用于GCM和CCM模式的AES加密的支持。
- 添加TLS扩展定义和AES密码组合[8]:2。所有TLS版本在2011年3月发布的RFC 6176中删除了对SSL的兼容,这样TLS会话将永远无法协商使用的SSL 2.0以避免安全问题。
TLS 1.3
TLS(安全传输层协议)是SSL(安全套接层协议)的升级版本,用于在两个通信应用程序之间提供保密性和数据完整性。TLS协议自标准化至今已有近20年的时间,自1999年TLS 1.0标准颁布,到后来的TLS 1.1(2006年)和目前得到广泛使用的TLS 1.2(2008年),TLS 是目前保障网络传输安全最重要的安全标准之一。TLS 1.3 加密协议是在 TLS 1.0 、TLS 1.1 、TLS 1.2版本基础上进行的升级和改造,也是迄今为止改动最大的一次,历经长达4年28次草案修改后,正式获得互联网工程指导委员会(IESG)批准问世。
https://blog.cloudflare.com/tls-1-3-overview-and-q-and-a/
https://github.com/tlswg/tls13-spec
Extensions
Spec:
h
TLSEXT_ALPN
上层协议协商,就是在握手过程中,标明TLS里面是什么协议,例如 HTTP2 就是 h2c
Encrypted Client Hello
Specification: h
Encrypted Client Hello (ECH) is a new extension for TLS that promises to significantly enhance the privacy of this critical Internet protocol. Today, a number of privacy-sensitive parameters of the TLS connection are negotiated in the clear. This leaves a trove of metadata available to network observers, including the endpoints' identities, how they use the connection, and so on.
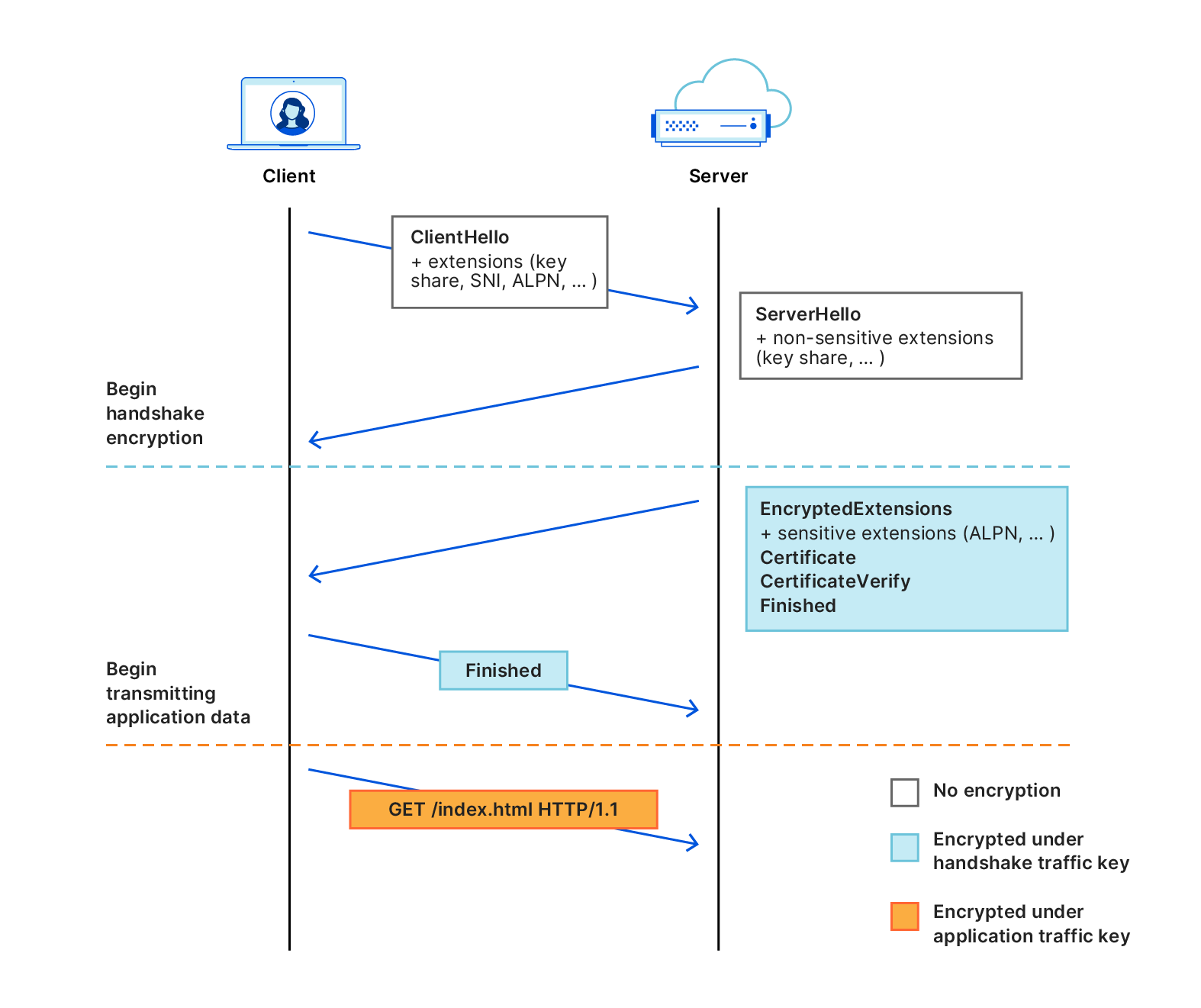
How to config ECH articles:
- https://cujo.com/blog/set-up-ech-website/
- h
t t p s : / / g u a r d i a n p r o j e c t . i n f o / 2 0 2 3 / 1 1 / 1 0 / q u i c k - s e t - u p - g u i d e - f o r - e n c r y p t e d - c l i e n t - h e l l o - e c h /
HTTPS DNS lookup sample:
Others:
Maximum Fragment Length Negotiation
主要用于嵌入式环境,需要客户端发送。
Certificate Status Request
OCSP ,OCSP 主要是为了减少客户端查询 证书撤销列表(Ceritificate Revoke List)的网络调用,而提出的。
Server Name Indication
由于在SNI(Server Name Indication)提出之前,TLS握手过程中没有字段标明客户端希望连接服务器端的哪个域名,这样如果一个服务器端口上有多个域名,服务器就无法给出正确的证书。随着ipv4地址空间紧张,这个问题越发突出。因此提出了SNI。
Session Ticket
Session Ticket,就是把 Session Cache 加密后存入客户端,这样服务器端就不需要任何存储了。
TLSEXT_SAFE_RENEGOTIATION
重协商
Implemention
https://webencrypt.org/openssl/ - OpenSSL
https://bearssl.org/ - BearSSL
https://github.com/rustls/rustls - Rustls
https://www.wolfssl.com/ - wolfSSL
https://www.gnutls.org/ - GnuTLS
https://curl.haxx.se/docs/ssl-compared.html
https://github.com/tlswg/tls13-spec/wiki/Implementations
Research
Configuration
Guide:
- https://www.eff.org/https-everywhere/deploying-https
- h
t t p s : / / p i x e l p r i v a c y . c o m / r e s o u r c e s / h o w - t o - e n c r y p t - y o u r - t r a f f i c /
Server side config samples: https://github.com/ioerror/duraconf
Tool
https://badssl.com/ - SSL Test
https://badgmssl.com/ - SM SSL Test
https://cipherli.st/ - strong cliphers
https://myssl.com/ - SSL/TLS安全评估报告
https://www.howsmyssl.com/ - client test
https://ssldecoder.org/ - SSL Decoder
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html - server test [dev]
https://observatory.mozilla.org/ - Observatory by Mozilla
https://mozilla.github.io/server-side-tls/ssl-config-generator/ [github] - Server Side TLS
https://github.com/april/tls-table - TLS Table
https://testssl.sh/ - Testing TLS/SSL encryption anywhere on any port [github]
$ nmap --script ssl-enum-ciphers -p 443 <host>
https://certificatemonitor.org/
https://webencrypt.org/illustrated-tls/ - The Illustrated TLS Connection, https://tls.ulfheim.net/ [github]
https://webencrypt.org/illustrated-tls13/ - The Illustrated TLSv1.3 Connection, https://tls13.ulfheim.net/ [github]
https://site.hatter.ink/illustrated-quic/ The Illustrated QUIC Connection, https://quic.ulfheim.net/ [github]
Certificate Authority
CA certificates extracted from Mozilla
https://curl.haxx.se/docs/caextract.html
Java CA
Import root CA to Java cacerts
keytool -trustcacerts \ -keystore $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/security/cacerts \ -storepass changeit \ -noprompt \ -importcert \ -file root-cert.pem
Reference
- h
t t p s : / / g i t h u b . c o m / a g l - h
t t p s : / / t l s f u n . d e / - h
t t p : / / w i k i . c a c e r t . o r g / S S L S c a n n e r - h
t t p s : / / z m a p . i o / s s l v 3 / - h
t t p s : / / g i t h u b . c o m / D i n o T o o l s / s s l s c a n - h
t t p s : / / w w w . h t b r i d g e . c o m / s s l / - h
t t p s : / / w w w . s s l l a b s . c o m / - h
t t p s : / / w i k i . m o z i l l a . o r g / C A : I n c l u d e d C A s - h
t t p s : / / w w w . g n u t l s . o r g / - h
t t p s : / / w w w . o p e n s s l . o r g / - h
t t p s : / / c r y p t o . s t a c k e x c h a n g e . c o m / q u e s t i o n s / 1 5 3 2 9 / t l s - s s l s - u s a g e - o f - n o n - e p h e m e r a l - d h - v s - d h e - h
t t p s : / / t l s . m b e d . o r g / k b / c r y p t o g r a p h y / e p h e m e r a l - d i f f i e - h e l l m a n - h
t t p s : / / t l s . m b e d . o r g / s u p p o r t e d - s s l - c i p h e r s u i t e s - h
t t p s : / / w i k i . m o z i l l a . o r g / S e c u r i t y / S e r v e r _ S i d e _ T L S - h
t t p s : / / w w w . i a n a . o r g / a s s i g n m e n t s / t l s - p a r a m e t e r s / t l s - p a r a m e t e r s . x h t m l - h
t t p s : / / g i t h u b . c o m / j m h o d g e s / h o w s m y s s l - h
t t p s : / / b u g s . c h r o m i u m . o r g / p / c h r o m i u m / i s s u e s / d e t a i l ? i d = 6 4 8 3 2 7 - h
t t p s : / / v i n c e n t . b e r n a t . i m / e n / b l o g / 2 0 1 1 - s s l - s e s s i o n - r e u s e - r f c 5 0 7 7 - h
t t p : / / w w w . r u a n y i f e n g . c o m / b l o g / 2 0 1 4 / 0 9 / i l l u s t r a t i o n - s s l . h t m l - h
t t p s : / / i m q u q u . c o m / p o s t / o p t i m i z e - t l s - h a n d s h a k e . h t m l - h
t t p s : / / g i t h u b . c o m / z q j f l a s h / s e c u r i t y - h t t p - h
t t p s : / / z h . w i k i p e d i a . o r g / w i k i / 傳 輸 層 安 全 協 議 - h
t t p s : / / r a y m i i . o r g / s / t a g s / s s l . h t m l - h
t t p s : / / s e c u r i t y . s t a c k e x c h a n g e . c o m / q u e s t i o n s / 9 4 3 9 0 / w h a t s - t h e - p u r p o s e - o f - d h - p a r a m e t e r s - h
t - IESG正式批准TLS 1.3协议,HTTPS加密性能提速t p s : / / w w w . w o s i g n . c o m / n e w s / 2 0 1 8 - 0 3 3 0 - 0 1 . h t m - h
t - TLS协议分析 与 现代加密通信协议设计(一)t p s : / / g a m e i n s t i t u t e . q q . c o m / c o m m u n i t y / d e t a i l / 1 0 1 8 6 6 - h
t - TLS协议分析 与 现代加密通信协议设计(四)t p s : / / g a m e i n s t i t u t e . q q . c o m / c o m m u n i t y / d e t a i l / 1 0 1 8 6 5